Tutorial on MRI-Guided Robot-Assisted Prostate Biopsy
Step 3: Register SmartTemplate to the scanner (world)
Open the python console (click the button in the menu bar)
FOR DOCKER USERS If you are running the Docker image, you can copy the contents of the contents via clipboard. To use it, click the small tab on the left of the browser window where the desktop of the Docker container is being displayed, click the clipboard button to open the clipboard text box, and paste the code there.
Then click the Python console on the 3D Slicer window, click the right mouse button to open the pull down menu, and choose paste.
In the python console, enter the folloing python codes in the python code. The code is also available python_console_commands.txt (View File).
# Get robot node
rosNode = slicer.util.getModuleLogic('ROS2').GetDefaultROS2Node()
robotNode = rosNode.GetRobotNodeByName('smart_template')
# Get robot_description
robot_description = slicer.util.getNode(robotNode.GetNodeReferenceID('parameter')).GetParameterAsString('robot_description')
# Get RobotToZFrame (from URDF robot_description)
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
root = ET.fromstring(robot_description)
zframe_orientation = root.find('./custom_parameters/zframe_orientation').get('value').strip()
zframe_position = root.find('./custom_parameters/zframe_position').get('value').strip()
rotation_values = list(map(float, zframe_orientation.strip().split()))
translation_values = list(map(float, zframe_position.strip().split()))
mat_ZFrameToRobot = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
for i in range(3): # Set rotation part (3x3)
for j in range(3):
mat_ZFrameToRobot.SetElement(i, j, rotation_values[3 * i + j])
for i in range(3): # Set translation part (last column)
mat_ZFrameToRobot.SetElement(i, 3, 1000*translation_values[i])
mat_ZFrameToRobot.SetElement(3, 3, 1.0)
t_RobotToZFrame = vtk.vtkTransform()
t_RobotToZFrame.SetMatrix(mat_ZFrameToRobot)
t_RobotToZFrame.Inverse()
# Get ZFrameToScanner (from ZFrame registration)
mat_ZFrameToScanner = vtk.vtkMatrix4x4()
ZFrameToScannerNode = slicer.util.getFirstNodeByName('COR_TSE_T2_COVER_ZFRAME-label-ZFrameTransform', className='vtkMRMLLinearTransformNode')
ZFrameToScannerNode.GetMatrixTransformToWorld(mat_ZFrameToScanner)
t_ZFrameToScanner = vtk.vtkTransform()
t_ZFrameToScanner.SetMatrix(mat_ZFrameToScanner)
# Calculate RobotToScanner transform (robot world pose)
t_RobotToScanner = vtk.vtkTransform()
t_RobotToScanner.Concatenate(t_ZFrameToScanner)
t_RobotToScanner.Concatenate(t_RobotToZFrame)
mat_RobotToScanner = t_RobotToScanner.GetMatrix()
# Create publisher and send RobotToScanner to \world_listener
pubWorld = rosNode.CreateAndAddPublisherNode('TransformStamped', '/world_pose')
world_msg = pubWorld.GetBlankMessage()
world_msg.SetTransform(mat_RobotToScanner)
pubWorld.Publish(world_msg)
This python code performs the following steps:
- Get the robot node from the scene
- Get the
robot_descriptionfrom the ROS2 topic publisher by SmartTemplate - Recover ZframeToRobot information from the URDF custom parameters
- Use the ZframeToScanner registration to calculate the final RobotToScanner transform (robot world pose)
- Create a ROS2 publisher and publish to the
\world_listenertopic (which is subscribed by SmartTemplate to send atf_static_broadcastto update the tf tree)
In the ROS2 terminal where the SmartTemplate was launched, you can read an indication that the world_pose_listener node was triggered by the \world_pose topic published by SlicerROS2, and this caused the tf_static_broadcaster to update the world transform:
[INFO] [<timestamp_value>] [world_pose_listener]: Updated static transform world -> base_link published.
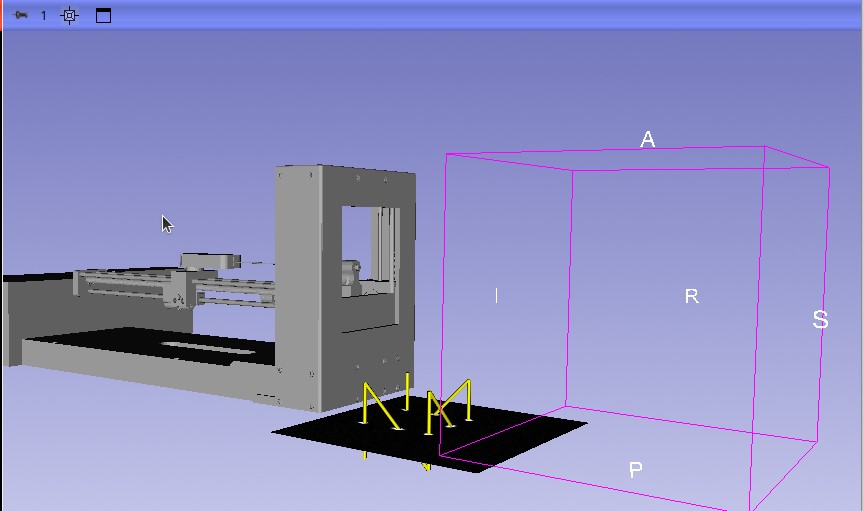
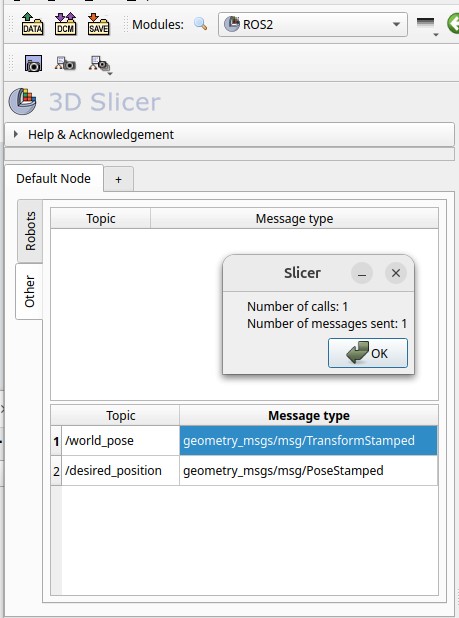
The SmartTemplate pose will automatically update to the registered pose with respect to the world (scanner). Also, observe the publisher we created in the SlicerROS2 GUI and the topic message just sent:
| ⬅️ Previous: Load SmartTemplate robot | Next: Make a straight needle insertion ➡️ | Back to Table of Contents ↩️ |